Cannabinoids 101: A Guide To The Basics
Published :
Apr 26, 2017
Categories :
Medical cannabis

A short overview of what cannabinoids are, how they work, and the best known compounds.
Cannabinoids are chemical compounds found in the marijuana plant that give cannabis its juice, buzz and effectiveness. They are why you get “high” if used recreationally, or "feel better” if you are ill.
They work by imitating or augmenting naturally occurring compounds produced by the human body to regulate or stimulate mood, hunger, feelings of pain, and the immune system. There are over 80 cannabinoids in marijuana – most of them still unstudied.
Cannabinoids are not just found in the cannabis plant however.
So-called “natural” cannabinoids, or endocannabinoids, are produced by the body itself. How plant and biologically produced cannabinoids work together within the mammalian endocannabinoid system is a subject of study that is just beginning to come into its own.
STIMULATION OF CANNABINOID RECEPTORS
When consumed, cannabinoids attach or “bind” to endocannabinoid receptors found in most parts of the body. Collectively, these receptors are referred to as the endocannabinoid system – which is now believed to be the fourth of the body’s most important regulatory systems. The endocannabinoid system also may act as a “master” regulatory switch as it's helping the other major systems of the body work better or more efficiently.
There are two types of cannabinoid receptors in the body – CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are mostly found in the central nervous system and are responsible for mediating the effects of cannabinoids in the brain. They are found mostly in the basal ganglia, hippocampus and cerebellum. They play an important role in regulating memory, mood, sleep, appetite and pain suppression. However, they also play a role in muscle control, thermoregulation, nausea control and controlling intraocular pressure. CB2 receptors, while also found in the brain, mostly exist in the immune system, the gastrointestinal system, and the peripheral nervous system. They may also play a role in cell proliferation. CB2 receptors are also found in immune cells and work to reduce inflammation. Because inflammation is also an immune response, it is believed to be a factor in many diseases, and thus CB2 receptor stimulation may also play a critical role in preventing diseases such as cancer.
Different types of cannabinoids work by stimulating cannabinoid receptors in specific areas of the body. The most known and studied cannabinoids are:
THC
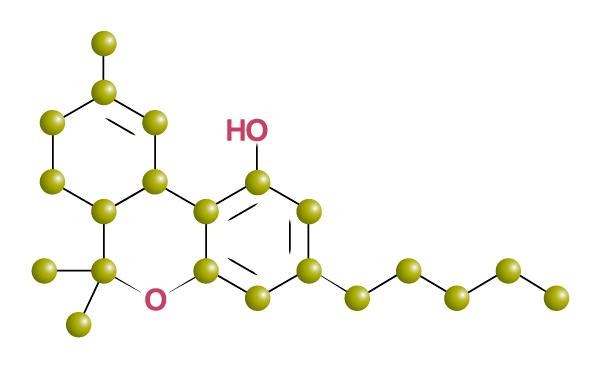
By far the best known and studied cannabinoid is THC – an abbreviation of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. It creates the “high” or psychoactive effect in recreational use. However, it is also the most effective cannabinoid studied so far in the treatment of chronic pain and muscular spasticity. Medical users frequently report, particularly after using cannabis for some time, that the psychoactive effect gradually disappears, leaving only symptomatic relief.
CBD
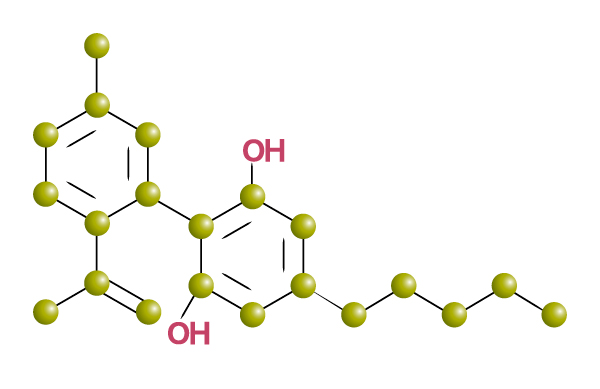
Cannabidiol, because it is not psychoactive, is also known as the “less controversial” cannabinoid. It is already legal in many jurisdictions where THC is not. When used medically, this cannabinoid is used to treat many of the same conditions that THC is used for. However because it does not produce the high, it is also used to treat children, particularly with cancer and epilepsy. It is also found, unlike THC (OK, neglectable amounts are present), in hemp.
CBC
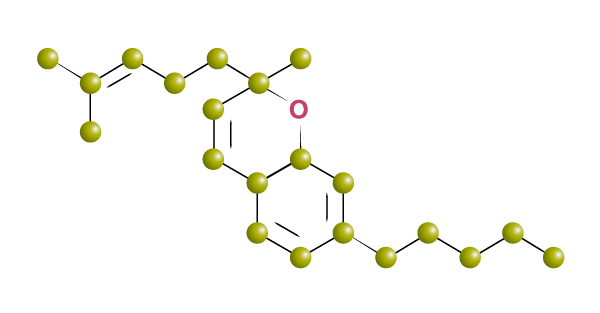
Cannabichromene is used in many cases interchangeably with CBD, although far less studied. As more is known about its effects, it may actually become more common than CBD. It is primarily used as an anti-inflammatory and anti-fungal, to treat tumours, and as an antidepressant. Because it may also encourage brain growth, it is now being studied as a treatment for Alzheimer’s. It is only found in tropical strains of cannabis.
CBN
Cannabinol is actually created by decomposing THC. If dried cannabis flower has been left sitting exposed to the open air, for example, the sample will have lots of this cannabinoid. High CBN marijuana has many uses, including as an appetite stimulant, an antibiotic and could potentially be helpful in treating the symptoms of degenerative motor neurone disease, such as ALS (Lou Gehrig’s disease.) It has also been used as an anti-asthmatic – primarily because of its anti-inflammatory properties, as well as a sedative, and to treat glaucoma because this cannabinoid has marked muscle relaxant and blood pressure impacts.
CBG
Cannabigerol is found early in the growth cycle of cannabis plants. It is not psychoactive, and like CBD, can also be found in hemp. It has already been found to be highly effective as both an anti-fungal and to treat psoriasis (a skin condition). It may also be that CBG is even more effective than THC in treating pain. This cannabinoid has also already been shown to have a marked impact on treating tumours and also works as a mild anti-depressant.
THCv
Tetrahydrocannabivarin, like THC, is psychoactive, although it has only about 20% of the capacity to make users feel euphoric. Research is also starting to indicate that THCv may mitigate some of the negative psychoactive impacts of THC. This cannabinoid has been used effectively as an anticonvulsant, and may even stimulate weight loss by helping to reduce body fat. THCv also works as a neuroprotective.
CBDv
Cannabidivarin is one of the lesser known cannabinoids and has not been studied as much as CBD itself. There are slight molecular differences in the two cannabinoids which also impact how the compound works. This cannabinoid appears to be most effective as both an anti-epileptic and to combat nausea.
Δ8 THC
This form of THC has one less “delta” than the more widely known THC. This makes it slightly less psychoactive than regular THC. It may also have neuroprotective and anti-anxiety properties. It has already been shown to have an anti-nausea effect and to increase appetite.
THCa AND CBDa
Both of the “a” cannabinoids are found in raw cannabis. As such they are most commonly found in nutrients or typically applied creams. Once THCa or CBDa are heated, the compounds are converted into the more regularly known forms of cannabinoids. THCa however, is not psychoactive. Both forms of these cannabinoids are used as anti-oxidants, anti-inflammatories and to improve intestinal and neural function.