Can CBD Treat Degenerative Disc Disease?
Published :
May 31, 2019
Categories :
Medical cannabis

Degenerative disc disease is a large contributor to back pain, a cause of chronic pain for many. CBD has been shown to attenuate this degeneration within animal models, and could be a possible treatment in the future.
CBD continues to gain recognition as a natural medicine as ever more scientific research and anecdotal accounts come rolling in. Otherwise known as cannabidiol, CBD is a non-psychotropic cannabinoid synthesised within the flowers of the cannabis plant. As one of the most researched cannabinoids, CBD has so far displayed anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antioxidant, neuroprotective, anti-tumour, and anticonvulsant properties.
CBD SHOWS PROMISE FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL CONDITIONS
CBD also shows potential in the treatment of various musculoskeletal pathologies. The compound interacts with the endocannabinoid system, a regulatory system within the human body comprised of various receptor types, including CB1 and CB2 receptors. CBD also interacts with GPR55, a cannabinoid receptor associated with increased bone mass in animal studies.
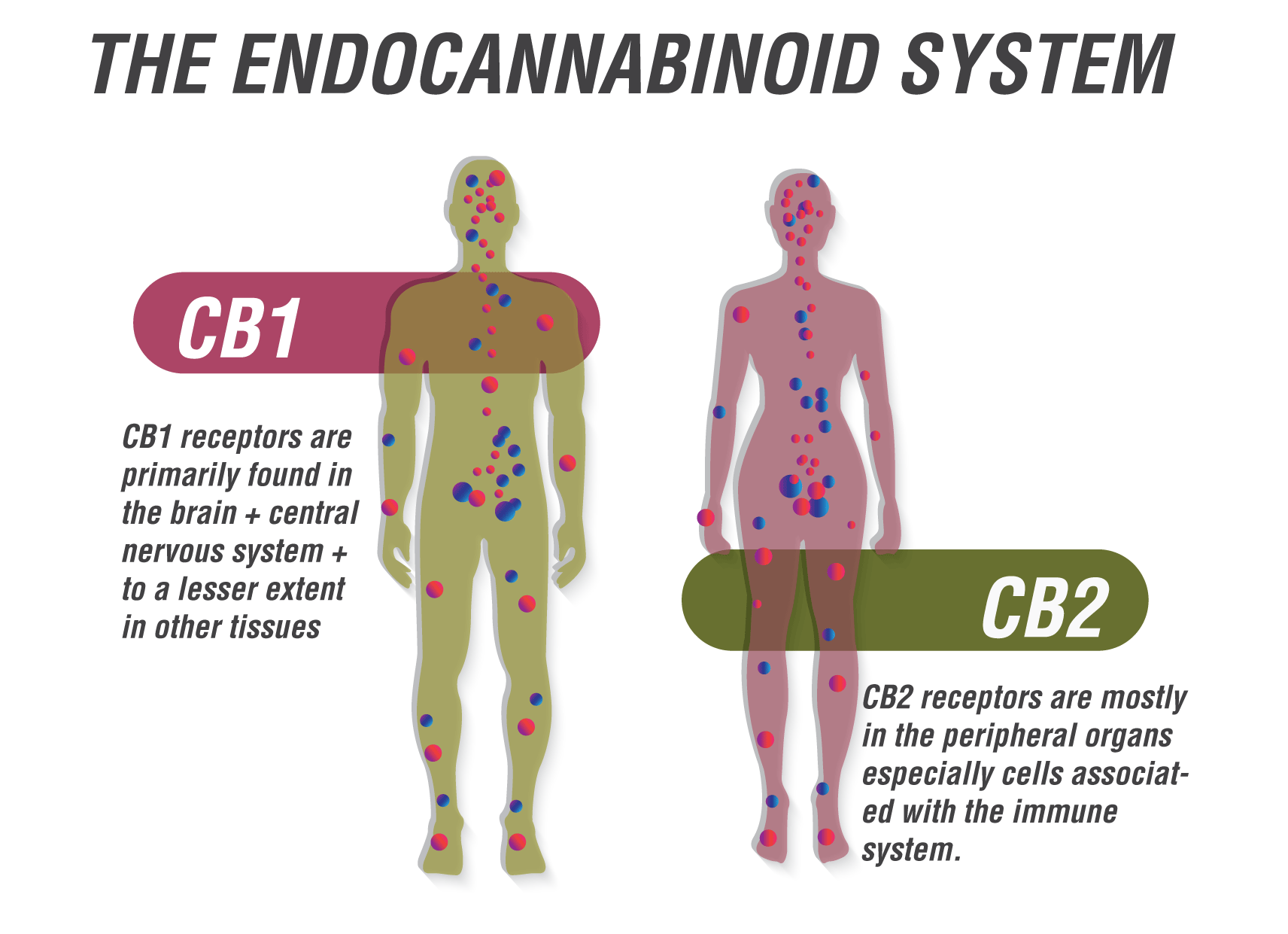
CAN CBD PREVENT OR TREAT DEGENERATIVE DISC DISEASE?
When it comes to preserving the discs of the spine, here too CBD displays promise. Research is ongoing regarding CBD’s potential as a future treatment for degenerative disc disease. Although current research has been performed using animal models, further human research could mark a breakthrough in this arena. Intervertebral disc degeneration is reported to be the main contributor to low back pain, a condition that affects large portions of the world's population.
Recent research suggests that CBD has a protective effect over intervertebral discs in vivo. However, before we dig into the data, let’s take a look at exactly what discs are and how they begin to degenerate.
ANATOMY 101: WHAT IS AN INTERVERTEBRAL DISC?
An intervertebral disc sits between two spinal vertebrae within the vertebral column and contributes to the formation of a fibrocartilaginous joint. These discs have multiple functions, including shock absorption for the spine, movement, and stability of the spine.
Each disc features an outer ring, or annulus fibrosus, composed of several layers of fibrocartilage made up of different types of collagen. Within this ring exists a gel-like centre containing loose fibres called the nucleus pulposus. It’s this gel-like substance that allows discs to absorb physical shock during movement and activity.
Many people will have heard of the so-called phenomenon of a “slipped disc”. What this actually means is that the gel-like fluid of the nucleus pulposus been forced against the annulus fibrosus to the point of protrusion or prolapse. This can be caused by physical trauma during activity or by chronic deterioration in the form of poor posture. The nucleus pulposus can herniate in lateral and posterior directions and cause symptoms such as numbness, pain, and loss of sensation due to pressing on nerves.
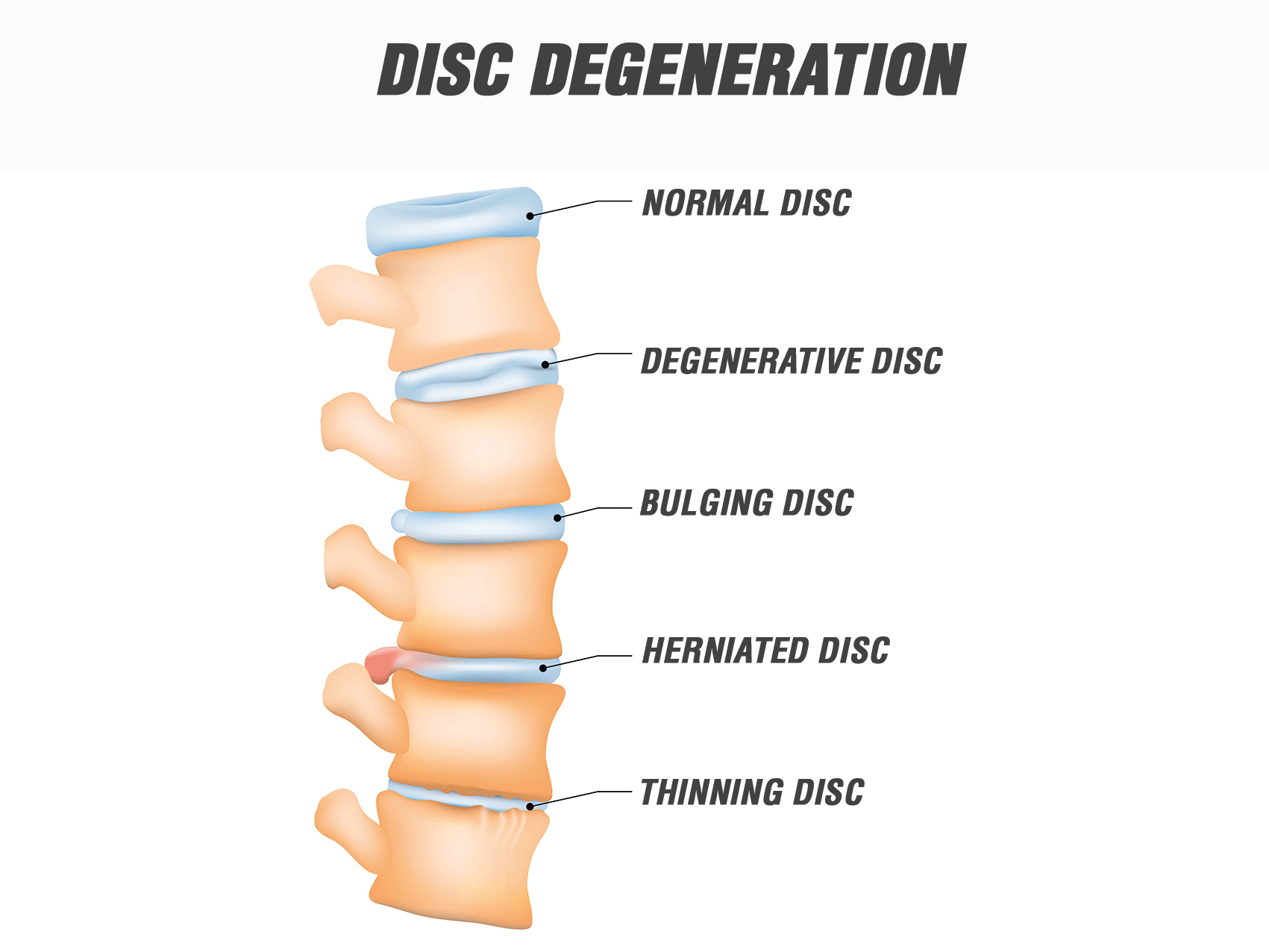
WHAT EXACTLY IS INTERVERTEBRAL DISC DISEASE?
Intervertebral disc disease is characterised by the gradual breakdown of one or more discs within the spine. Disc degeneration is a natural part of ageing, with around 25% of individuals displaying evidence of degeneration before the age of 40. During this process, the nucleus pulposus begins to lose some of its water content and the annulus fibrosus becomes more prone to tearing, resulting in possible herniation.
Degeneration and subsequent herniation can lead to spinal nerve compression, which can result in pain, weakness, and numbness in the extremities. As degeneration continues, bone spurs can form at the edge of individual vertebra, causing further compression of nerves, and possibly causing issues with walking and bladder/bowel control.
RESEARCH SHOWS CBD MAY PROVE TO BE A FUTURE TREATMENT
CBD has already shown early efficacy as a potential musculoskeletal medicine, and more evidence is mounting. A 2014 study published within the journal PLoS One investigated the protective effect of CBD on lesion-induced intervertebral disc degeneration within rats.
Researchers first induced damage to intervertebral discs via needle puncture to create a lesion. The rats were then divided into three sub-groups, with 6–7 animals in each group. Each group was then administered a different dose of CBD via injection: 30, 60, and 120 nmol.
After administration, the researches used MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and microscope analysis to examine the induced injuries. The results of the analysis revealed no improvements within the 30 and 60 nmol groups. However, improvement in lesion damage was seen in the 120 nmol group in both MRI and microscope imaging up to 15 days afterwards.
These results led the authors to state that the study revealed the anti-degenerative effects of CBD injection at 120 nmol. Although more research is required in this domain, such results indicate the future use of CBD for disc degeneration treatment.
CBD MAY ALSO ASSIST WITH SIDE EFFECTS OF DEGENERATIVE DISC DISEASE
Inflammation plays a large role within the process of degenerative disc disease. Although specific studies need to be performed to find a correlation, CBD has been shown to exert anti-inflammatory effects by interfacing with cannabinoid and adenosine receptors.
Pain also plays a large role in degenerative disc disease, particularly neuropathic pain that stems from compression of nerves due to herniation. CBD may help to relieve this side effect as there is some evidence to suggest cannabinoids are effective in reducing neuropathic pain.
Finally, CBD may help to tackle some of the psychological symptoms associated with degenerative disc disease. The compound displays anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effects that can help boost the quality of life of sufferers.